By TI 538
The LM339 is an integrated circuit (IC), also commonly known as a comparator. It consists of multiple comparators, usually four, packaged on a single chip. Each comparator has two input pins (non-inverting input and inverting input) and one output pin.
The LM339 voltage comparator chip is equipped with four independent voltage comparators. Various voltage comparator circuits and oscillator circuits can be easily composed using LM339.
Ⅰ.Structure of LM339
Basic structure:
Power pins: LM339 usually has two power pins, +Vcc and -Vc. These pins are used to provide the supply voltage so that the LM339 can operate properly.
Four comparators: LM339 contains four independent comparators inside, each comparator has two input pins (non-inverting input and inverting input) and one output pin. These four comparators can perform independent comparison operations simultaneously.
Output Pin: Each comparator has an output pin that is used to produce the comparison result. When the non-inverting input voltage is greater than the inverting input voltage, the output pin is usually at a high level (usually a positive supply voltage), and vice versa is at a low level (usually a negative supply voltage or near zero voltage).
Reference voltage pin: Typically, LM339 also includes a reference voltage pin (Vref), which is used to provide a reference voltage for comparison operations. This pin is typically connected to a non-inverting input pin to allow comparison of the input signal to a reference voltage.
Internal circuit: Inside the chip, LM339 contains circuits related to the comparator operation, including amplifiers, feedback circuits, and switching circuits. These circuits enable the LM339 to perform comparison operations and produce corresponding outputs based on the relative magnitudes of the input signals.
The LM339 is similar to an op amp with non-adjustable gain. Each comparator has two inputs and one output. One of the two input terminals is called the non-inverting input terminal, represented by "+", and the other is called the inverting input terminal, represented by "-". When used to compare two voltages, add a fixed voltage to any input end as the reference voltage (also called the threshold level, which can select any point in the LM339 input common mode range), and add a signal voltage to be compared to the other end.
When the voltage at the "+" terminal is higher than the "-" terminal, the output tube is cut off, which is equivalent to an open circuit at the output terminal. When the "-" terminal voltage is higher than the "+" terminal, the output tube is saturated, which is equivalent to the output terminal being connected to a low potential. A voltage difference of more than 10mV between the two input terminals can ensure that the output can be reliably converted from one state to another. Therefore, it is ideal to use LM339 in situations such as weak signal detection.
The output terminal of LM339 is equivalent to a transistor without a collector resistor. When used, a resistor (called a pull-up resistor, choose 3-15K) must be connected from the output terminal to the positive power supply. Pull-up resistors with different values will affect the value of the high potential at the output end. Because when the output transistor is turned off, its collector voltage basically depends on the value of the pull-up resistor and the load. In addition, each comparator (including analog comparator) is allowed to be connected together during operation.
Ⅱ.Specification parameters of LM339
•Output voltage: 36 V
•Power supply voltage: 2V ~ 36V
•Operating temperature: 0℃ ~ 70℃
•LM339 Vcc has a wide voltage range, single power supply is 2-36V, dual power supply voltage is ±1V-±18V
•Common mode voltage range: Vic=0~Vcc-1.5V
•Current consumption: Icc=1.3mA
•Input offset voltage: VIO=±2mV
•Package: DIP14, SOP14
Ⅲ. Pins of LM339
•Pin configuration
1.OUTPUT2 (pin 1): output terminal 2
2.OUTPUT1 (pin 2): output terminal 1
3.V+ (Pin 3): Positive power supply pin. Typically connected to the positive supply voltage, powering the LM339.
4.INPUT1- (Pin 4): Inverting input terminal 1
5.INPUT1+ (pin 5): non-inverting input terminal 1
6.INPUT2-(Pin 6): Inverting input terminal 2
7.INPUT2+ (pin 7): non-inverting input terminal 2
8.INPUT3-(Pin 8): Inverting input terminal 3
9.INPUT3+ (pin 9): non-inverting input terminal 3
10.INPUT4- (Pin 10): Inverting input terminal 4
11.INPUT4+ (Pin 11): Non-inverting input terminal 4
12.GND (pin 12): power ground
13.OUTPUT4 (pin 13): output terminal 4
14.OUTPUT3 (pin 14): output terminal 3

•Pin connections
1. Connect the positive supply and ground: First, connect the positive supply of the circuit to the positive supply pin of the LM339 (usually pin 14 or pin 1, depending on the package type) and the ground to the negative supply pin ( Typically pin 7 or pin 8, depending on package type). In this way LM339 will get the necessary power supply.
2. Connect the input signals: Connect the two input signals to be compared to the non-inverting input pin (IN+, usually pin 3, pin 7, pin 11, pin 13) and the inverting input pin of each comparator. Input pins (IN-, usually pin 2, pin 6, pin 10, pin 12). The voltage of the input signal will be compared between these pins.
3. Set the reference voltage: If you need to compare with the reference voltage, connect the reference voltage to the VREF pin of the corresponding comparator (usually pin 4, 8, 5, or 9). This step is optional, if a reference voltage is not required, the VREF pin can be left floating or connected to ground.
4. Connect the output signals: Connect the output pin (OUT, usually pin 4, pin 8, pin 11, pin 14) of each comparator to the corresponding output device or circuit. The output signal will change based on the voltage relationship between the comparator inputs.
5. Power supply: Apply the appropriate supply voltage to the positive supply pin (VCC+), usually between +5V and +30V, depending on your application needs.
6. Ground connection: Make sure the ground pin of LM339 is connected to the corresponding ground or negative power supply.
Ⅳ.Application of LM339
1. Current measurement: By placing a small resistor in the path of the current to be measured, the current can be converted into voltage, and then the LM339 is used to detect the voltage and achieve current measurement.
2. Sweeping robot
3. Server PSU
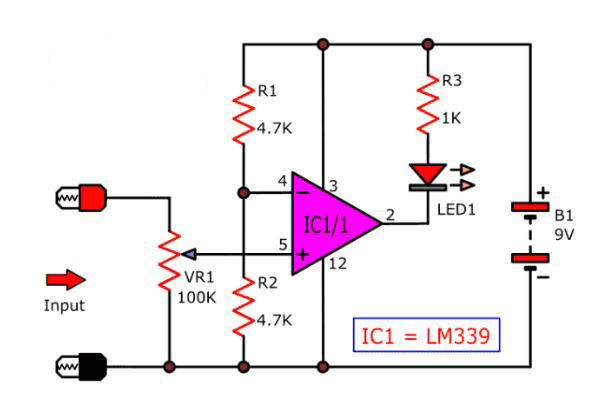
4. Voltage comparison: The main purpose of LM339 is as a voltage comparator. This circuit can compare two input voltages. If one set of voltages is larger, the output is high level. If one set of voltages is smaller, the output is low level. It is used to detect whether the voltage reaches or exceeds a certain threshold, such as battery voltage monitoring, power supply voltage monitoring, etc.
5. Switch control: LM339 can be used in switch control applications, such as controlling relays, switching circuits or alarm devices based on the state of the input signal.
6. Motor driver
7. Oscillator and waveform generator: LM339 can be configured as a ramp wave oscillator or a square wave oscillator for generating signals with adjustable frequency.
8. Level conversion: It can be used to convert signals of different levels into digital signals for input to digital systems.
9. Temperature measurement: By using a temperature sensor to convert temperature into a voltage signal, LM339 can be used to implement temperature measurement and monitoring.
10. Voltage window comparison: LM339 can be configured as a voltage window comparator to detect whether the input signal is within a specified voltage range.
11. Light intensity measurement: Combined with a photosensitive diode or photodiode, the LM339 can be used to measure the intensity of light or detect the presence or absence of light.
12. Power failure detection: used to detect whether the power supply voltage is within the normal range to trigger fault protection or alarm.
13. Analog signal processing: In various analog signal processing applications, such as filtering, sampling and continuous monitoring, the LM339 can be used to compare and process analog signals.
Ⅴ.Principle of LM339
1. Input signal comparison: Each comparator of LM339 has two input pins, one is a non-inverting input (IN+) and the other is an inverting input (IN-). The LM339 compares the voltage levels of these two input signals.
2. Reference voltage: LM339 also usually has a reference voltage pin (VREF), which allows you to set a reference voltage. If a reference voltage is used, the comparator compares the input signal to this reference voltage. If no reference voltage is used, the comparator compares the input signal to the voltage connected to the inverting input (IN-).
3. Output state: Depending on the comparison result, the output pin (OUT) of LM339 will be in a high level or a low level state. The specific status depends on the following situations:
If the voltage at the non-inverting input (IN+) is less than the voltage at the inverting input (IN-) (or the reference voltage, if a reference is used), the output will be in a low state (usually equal to the negative supply voltage or close to zero voltage).
If the voltage at the non-inverting input (IN+) is greater than the voltage at the inverting input (IN-) (or the reference voltage, if a reference is used), the output will be in a high state (usually equal to the positive supply voltage).
4. Multiple comparators: LM339 usually contains four independent comparators, each of which can perform the above comparison operations. This allows the LM339 to compare multiple sets of input signals simultaneously.

Ⅵ.Alternate model of LM339
1.LM393: LM393 is a low-power version of LM339 and is usually used in low-power applications. It is also a quad comparator with similar pin configuration and functionality.
2.LM311: LM311 is a single comparator instead of a quad, but it has higher speed and lower input bias current. If you only need one comparator, the LM311 may be a good choice.
3.LM324: LM324 is a quad operational amplifier that is also commonly used in comparator applications. It has four amplifiers instead of four comparators, but can be used as comparators, especially in some low-frequency applications.
4.LT1016: LT1016 is a high-speed comparator suitable for applications requiring fast response time. It has faster switching speeds than some common general-purpose models.
5.LM339A: LM339A is an enhanced version of LM339 with lower input bias current and higher input voltage range. It may be more suitable in certain precision applications.
6.LM311: LM311 is a high-speed comparator widely used in high-frequency applications and analog circuits.
7.MAX964: MAX964 is a precision voltage comparator with low power consumption and high accuracy. It is suitable for applications requiring high-precision comparisons.
8.MC34001: MC34001 is a general-purpose single-channel comparator with high speed and low power consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.What is the voltage range of LM339?
Typical voltage is 2V to 36V. Split supplies can be used as long as the voltage between V+ and V– is between 2V and 36V. A 0.1µF bypass capacitor should be used between the power supply pins or between the power supply pins and ground as close as possible to the device. V– (VSS): Negative supply.
2.What is the function of LM339?
The LM339N circuit is used in applications where two voltage signals need to be compared. In addition, the device is equipped with four on-board comparators that can compare four pairs of voltage signals at a time.
3.How to use LM339 correctly?
Determine the appropriate supply voltage range, then connect the positive supply pin to the positive supply voltage and the negative supply pin to the negative supply or ground. Make sure the power supply voltage is within the range specified in the specification sheet. Connect the output pin (OUT) of each comparator to the device or circuit that needs to be monitored or controlled. The outputs can be connected into other digital or analog circuits to achieve the desired function, such as controlling relays, LEDs, alarms, etc.